License Notice
This codebase and its associated model weights are released under FISH AUDIO RESEARCH LICENSE. Please refer to LICENSE for more details. We will take action against any violation of the license.
Legal Disclaimer
We do not hold any responsibility for any illegal usage of the codebase. Please refer to your local laws about DMCA and other related laws.
Quick Start
For Human
Here are the official documents for Fish Audio S2, follow the instructions to get started easily.
[!IMPORTANT] For SGLang server, please read SGLang-Omni README.
For LLM Agent
Install and configure Fish-Audio S2 by following the instructions here: https://speech.fish.audio/install/
Fish Audio S2
Best text-to-speech system among both open source and closed source
Fish Audio S2 is the latest model developed by Fish Audio. Trained on over 10 million hours of audio across approximately 50 languages, S2 combines reinforcement learning alignment with a Dual-Autoregressive architecture to generate speech that sounds natural, realistic, and emotionally rich.
S2 supports fine-grained inline control of prosody and emotion using natural-language tags like [laugh], [whispers], and [super happy], as well as native multi-speaker and multi-turn generation.
Visit the Fish Audio website for live playground. Read the blog post for more details.
Model Variants
| Model | Size | Availability | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| S2-Pro | 4B parameters | HuggingFace | Full-featured flagship model with maximum quality and stability |
More details of the model can be found in the technical report.
Benchmark Results
| Benchmark | Fish Audio S2 |
|---|---|
| Seed-TTS Eval — WER (Chinese) | 0.54% (best overall) |
| Seed-TTS Eval — WER (English) | 0.99% (best overall) |
| Audio Turing Test (with instruction) | 0.515 posterior mean |
| EmergentTTS-Eval — Win Rate | 81.88% (highest overall) |
| Fish Instruction Benchmark — TAR | 93.3% |
| Fish Instruction Benchmark — Quality | 4.51 / 5.0 |
| Multilingual (MiniMax Testset) — Best WER | 11 of 24 languages |
| Multilingual (MiniMax Testset) — Best SIM | 17 of 24 languages |
On Seed-TTS Eval, S2 achieves the lowest WER among all evaluated models including closed-source systems: Qwen3-TTS (0.77/1.24), MiniMax Speech-02 (0.99/1.90), Seed-TTS (1.12/2.25). On the Audio Turing Test, 0.515 surpasses Seed-TTS (0.417) by 24% and MiniMax-Speech (0.387) by 33%. On EmergentTTS-Eval, S2 achieves particularly strong results in paralinguistics (91.61% win rate), questions (84.41%), and syntactic complexity (83.39%).
Highlights
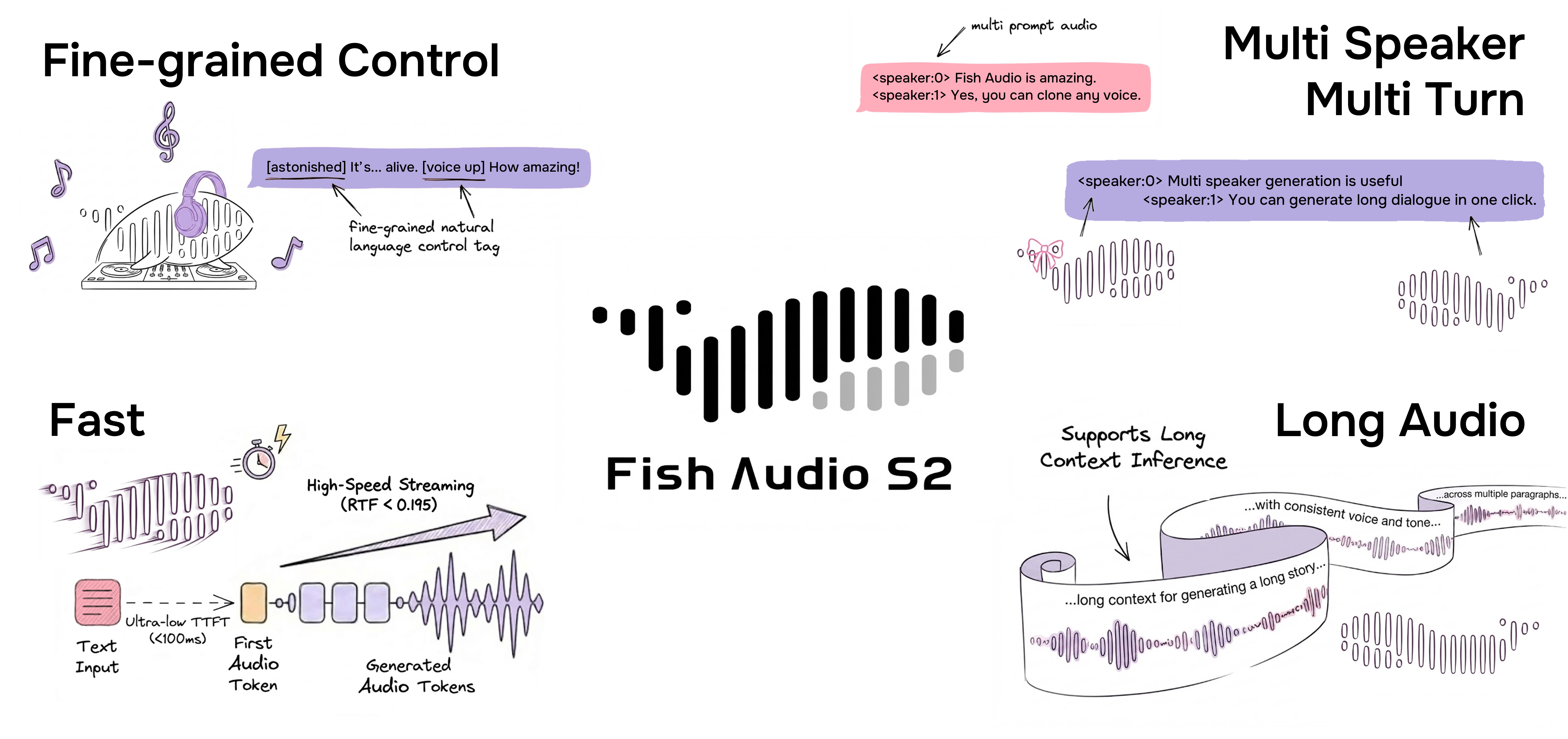
Fine-Grained Inline Control via Natural Language
S2 enables localized control over speech generation by embedding natural-language instructions directly at specific word or phrase positions within the text. Rather than relying on a fixed set of predefined tags, S2 accepts free-form textual descriptions — such as [whisper in small voice], [professional broadcast tone], or [pitch up] — allowing open-ended expression control at the word level.
Dual-Autoregressive Architecture
S2 builds on a decoder-only transformer combined with an RVQ-based audio codec (10 codebooks, ~21 Hz frame rate). The Dual-AR architecture splits generation into two stages:
- Slow AR operates along the time axis and predicts the primary semantic codebook.
- Fast AR generates the remaining 9 residual codebooks at each time step, reconstructing fine-grained acoustic detail.
This asymmetric design — 4B parameters along the time axis, 400M parameters along the depth axis — keeps inference efficient while preserving audio fidelity.
Reinforcement Learning Alignment
S2 uses Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) for post-training alignment. The same models used to filter and annotate training data are directly reused as reward models during RL — eliminating distribution mismatch between pre-training data and post-training objectives. The reward signal combines semantic accuracy, instruction adherence, acoustic preference scoring, and timbre similarity.
Production Streaming via SGLang
Because the Dual-AR architecture is structurally isomorphic to standard autoregressive LLMs, S2 directly inherits all LLM-native serving optimizations from SGLang — including continuous batching, paged KV cache, CUDA graph replay, and RadixAttention-based prefix caching.
On a single NVIDIA H200 GPU:
- Real-Time Factor (RTF): 0.195
- Time-to-first-audio: ~100 ms
- Throughput: 3,000+ acoustic tokens/s while maintaining RTF below 0.5
Multilingual Support
S2 supports high-quality multilingual text-to-speech without requiring phonemes or language-specific preprocessing. Including:
English, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabics, German, French...
AND MORE!
The list is constantly expanding, check Fish Audio for the latest releases.
Native Multi-Speaker Generation
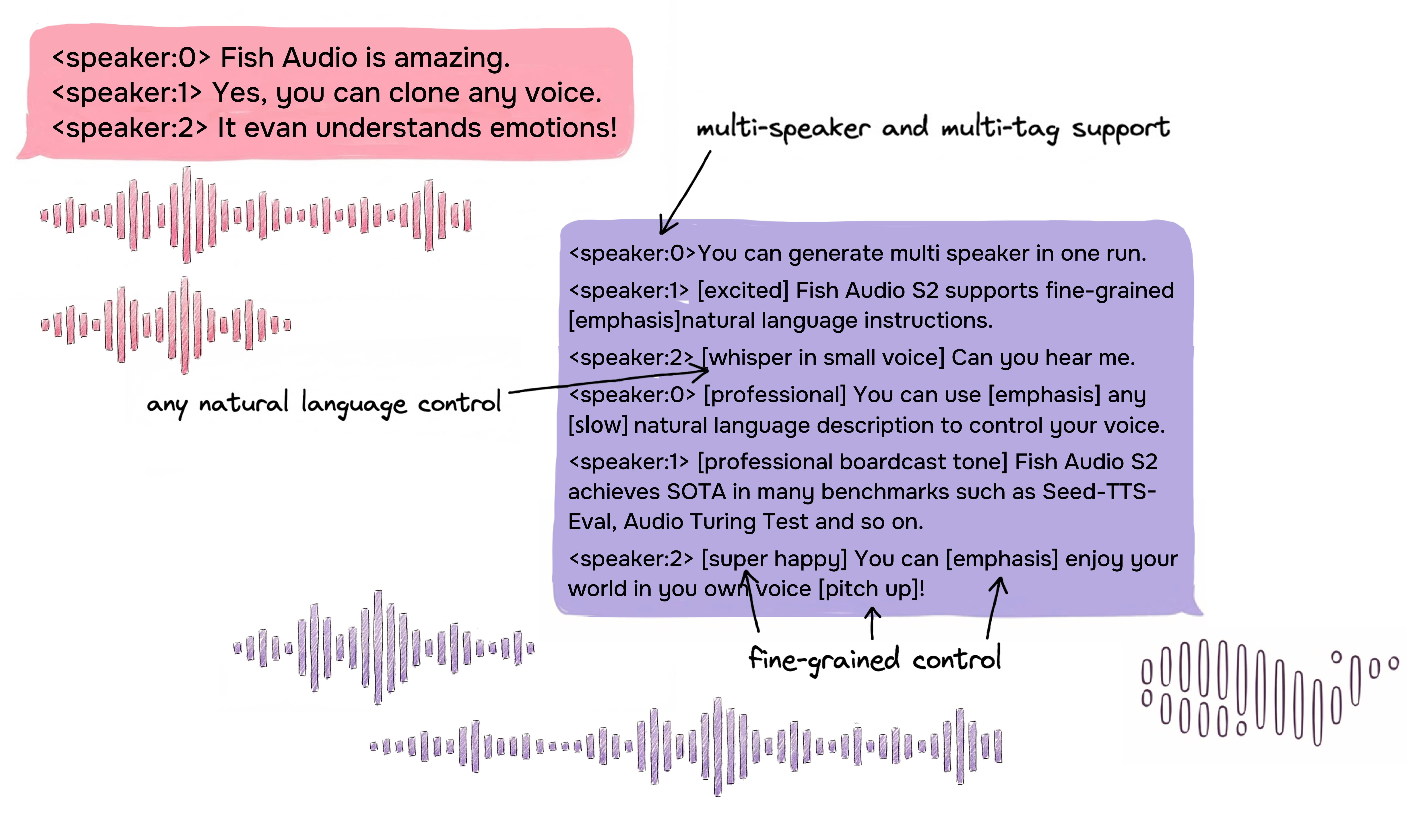
Fish Audio S2 allows users to upload reference audio with multi-speaker, the model will deal with every speaker's feature via <|speaker:i|> token. Then you can control the model's performance with the speaker id token, allowing a single generation to include multiple speakers. You no longer need to upload reference audio separately for each speaker.
Multi-Turn Generation
Thanks to the expansion of the model context, our model can now use previous information to improve the expressiveness of subsequent generated content, thereby increasing the naturalness of the content.
Rapid Voice Cloning
Fish Audio S2 supports accurate voice cloning using a short reference sample (typically 10–30 seconds). The model captures timbre, speaking style, and emotional tendencies, producing realistic and consistent cloned voices without additional fine-tuning. Please refer to SGLang-Omni README to use the SGLang server.
Credits
Tech Report
@misc{fish-speech-v1.4,
title={Fish-Speech: Leveraging Large Language Models for Advanced Multilingual Text-to-Speech Synthesis},
author={Shijia Liao and Yuxuan Wang and Tianyu Li and Yifan Cheng and Ruoyi Zhang and Rongzhi Zhou and Yijin Xing},
year={2024},
eprint={2411.01156},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.SD},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.01156},
}
@misc{liao2026fishaudios2technical,
title={Fish Audio S2 Technical Report},
author={Shijia Liao and Yuxuan Wang and Songting Liu and Yifan Cheng and Ruoyi Zhang and Tianyu Li and Shidong Li and Yisheng Zheng and Xingwei Liu and Qingzheng Wang and Zhizhuo Zhou and Jiahua Liu and Xin Chen and Dawei Han},
year={2026},
eprint={2603.08823},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.SD},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2603.08823},
}





